Which Best Describes How Penicillin Acts as an Antibiotic
Which best describes what happens when an antibiotic is applied to a population of bacteria. Antibiotics remove chloroplast from plant cells to cause starvation antibiotics increase the rate of dna replication human cells by forming nucleotides antibiotics and interfere with transport of intracellular and extracellular materials antibiotics decrease the rate of.

Which Of The Following Best Describes The Change In The Percent Of Penicillin Resistant S Aureus Bacteria Since 1940
Entry into the body of pathogenic microbes usually bacteria and the response of the bodys immune system to that invasion.

. Infections spread before treatment is available. Penicillin and other β-lactam antibiotics act by inhibiting penicillin-binding proteins which normally catalyze cross-linking of bacterial cell walls. It may cause irreversible vestibular damage after a long-term use E.
Bacteriostatic antibiotics limit the growth of bacteria by interfering with bacterial protein production DNA replication or other aspects of bacterial cellular metabolism. A general term for drugs that kill or inhibit the actions of microbes. Which best describes the crisis related to antibiotics.
This class includes penicillin derivatives cephalosporins monobactams and carbapenems. β-lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics characterized by having a β-lactam ring in their molecular structures. Which of the following best describes gentamicin.
Statement best describes how antibiotics affect cellular homeostasis. It takes too much time to develop effective antibiotics. And since peptidoglycan is not found in human cells penicillin is selectively toxic and does not harm us when we take it.
Specifically the drugs prevent the bacteria from synthesizing a molecule in the cell wall called peptidoglycan. Penicillin binds to penicillin binding protein PBP receptor on the surface of bacterial cell wall. Which best describes the action of penicillin and other beta-lactam containing antibiotics They disrupt peptidases that cross-ling glycan molecules of the bacterial cell wall They create holes in the pospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane They disrupt the 30S ribosomal subunit They create mutations in DNA molecules O All of the above are TRUE.
Some are highly specialised and are only effective against certain bacteria. Which best describes the mechanism of action of fluroquinolones. Multiple Choice It disrupts probelin synthesis in nonresistant bacteria.
It is becoming too expensive to manufacture effective antibiotics. Mechanism of penicillin inhibition. The bacteria develops resistance to the antibiotic in direct response to its application.
The penicillin class contains five groups of antibiotics. It inhibits cell wall synthesis by inhibiting transpeptidation D. The bacterias genetic material mutates in response to the antibiotic resulting in resistance.
It has poor post-antibiotic effect B. Herbal antibiotics have been used for centuries by herbalists for everything from fighting disease speeding up wound healing fighting off colds and flus treating respiratory problems and fighting infections. It is a narrow spectrum antibiotic.
Which of the following is the correct mechanism for how Polymyxins act as antibiotics. There are two main ways in which antibiotics target bacteria. How do antibiotics work.
Penicillin is part of the beta-lactam class of antibiotics. There are several antibiotics in the penicillin class. Today however with more and more people looking to return to more.
Which of the following antibiotics are best known to be used for acne. β-lactam antibiotics are administered for the prophylaxis and treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible organisms. Many antibiotics including penicillin work by attacking the cell wall of bacteria.
Aminopenicillins antipseudomonal penicillins beta-lactamase inhibitors natural penicillins and the penicillinase resistant penicillins. Some antibiotics get rid. Penicillin and most other β-lactam antibiotics act by inhibiting penicillin-binding proteins which normally catalyze cross-linking of bacterial cell walls.
Despite the abundance of various forms of antibiotics they function in basically two ways. Many of these herbs have been put on the back shelf since the appearance of synthetic antibiotics. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of the antibiotic streptomycin.
It has antagonistic effect on penicillin when used together C. Experts credit Alexander Fleming with discovering penicillins. Bacteria are increasingly resistant to antibiotics used to treat and eradicate infections.
Penicillin belongs to the beta-lactam family of antibiotics the members of which. The chemical structure of penicillin is triggered with a very precise pH-dependent directed mechanism affected by a unique spatial assembly of molecular components which can activate by protonation. PBP is the receptor for substrate peptidoglycan precursor in bacteria.
Another name for this class is the beta-lactam antibiotics referring to their structural formula. These bacteria are sometimes the cause of upper respiratory infections urinary tract infections and skin infections among others. Penicillin works by interfering with bacteria cell walls.
Antibiotics penicillin acts as alternative substrate and binds to PBP receptor and then inhibits transpeptidase which results in inhibition. Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic prescribed to treat staphylococci and streptococci bacterial infections. Penicillin is bactericidal because it directly kills bacteria.
You just studied 40 terms. It disrupts protein synthesis in resistant bacteria Streptomycin creates mutations in bacteria which cause them to become resistant Streptomycin inhibits cell wall synthesis in all bacterial. Others known as broad-spectrum antibiotics attack a wide range of bacteria including ones that are beneficial to us.
These antibiotics are effective against many different types of staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections. Alexander Fleming is credited with the discovery of antibiotics by finding the natural antibiotic penicillin.
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis by blocking transpeptidation.

Mcb Test 1 Chapter 1 Summary Chapter 4 5 6 And 7 Homework 1 Questions For Dr Madison S Studocu

Solved Question 15 2 23 Points Which Of The Following Best Chegg Com

Solved Antibiotic Resistance Develops In An Organism As A Chegg Com

Micro Homework 9 Ch 20 Flashcards Quizlet

Answered Which Of The Following Best Describes Bartleby

Solved Penicillin And Other Beta Lactam Antibiotics Are Chegg Com

Solved Which Of The Following Best Describes The Mechanism Chegg Com

Solved The Mechanism Of Action Of Penicillin As An Chegg Com

Micro Homework 9 Ch 20 Flashcards Quizlet

Solved Penicillin Is An Enzyme Inhibiting Antibiotic That Chegg Com

Solved Penicillin Is An Antibiotic That Kills Bacteria By Chegg Com

Micro Homework 9 Ch 20 Flashcards Quizlet
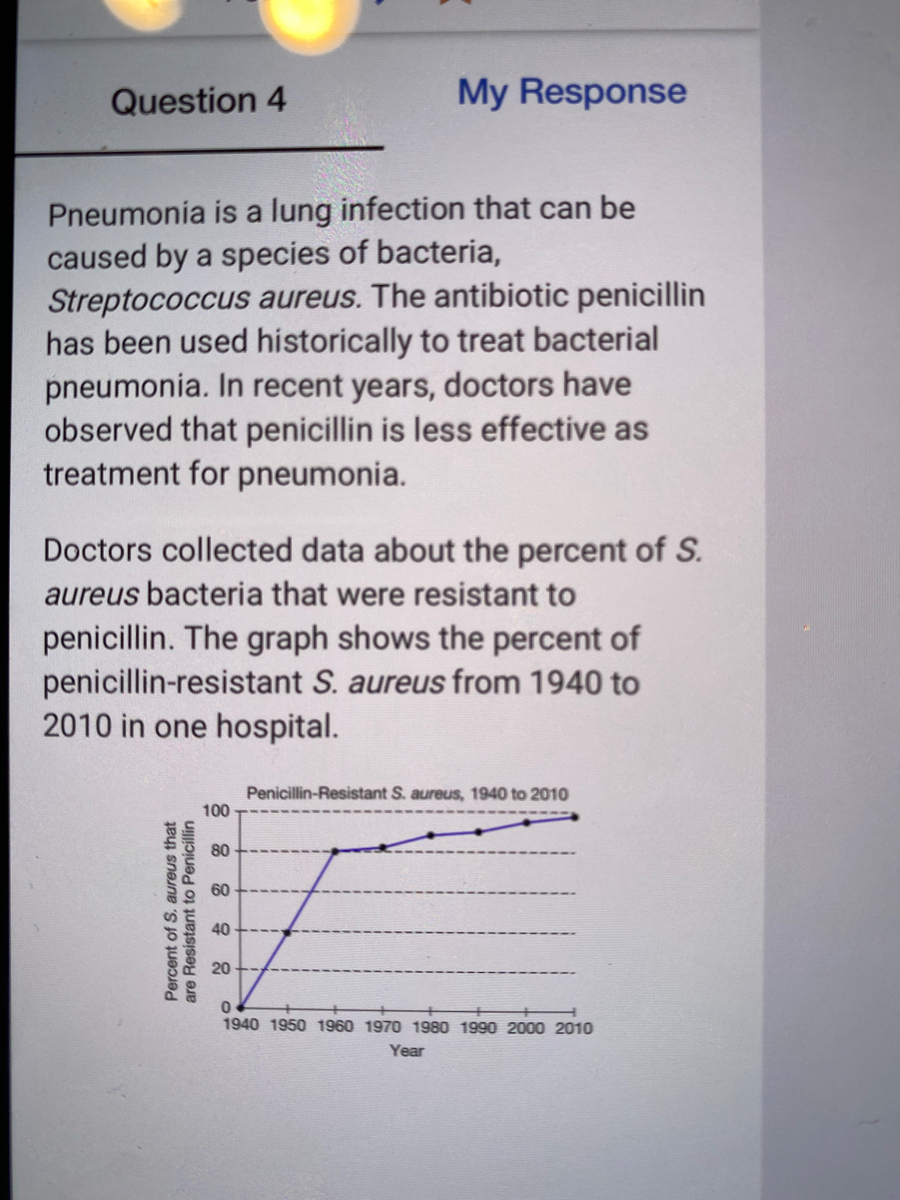
Answered Which Of The Following Best Describes Bartleby

Solved Bacteria And Antibiotics 9 Record The Diameter Of Chegg Com
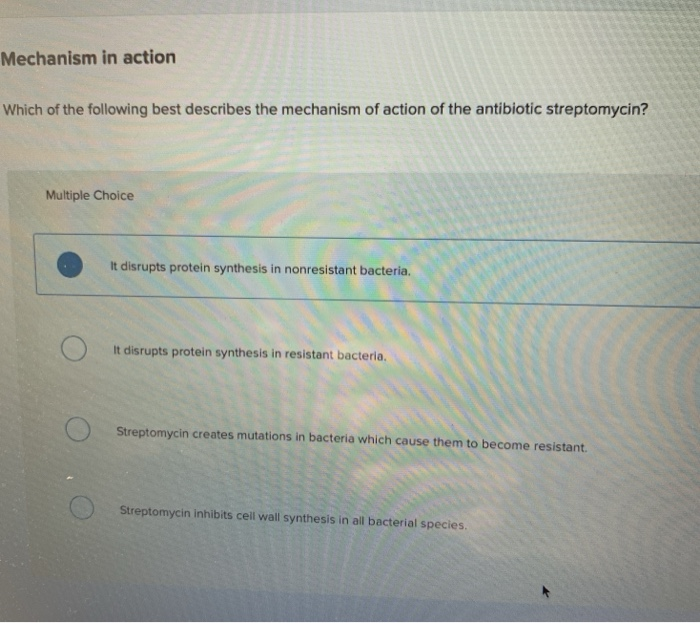
Solved Mechanism In Action Which Of The Following Best Chegg Com

Question 1 The Purpose Of The Kirby Bauer Disk Chegg Com

Solved Penicillin And Other Beta Lactam Antibiotics Are Chegg Com

Pharmacology Board Review Questions 1 50

Solved 18 The Mode Of Action Of An Antimicrobial Agent Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment